Describe the Characteristics of Four Different Family Structures
Family unit: Meaning, Characteristics, Part and Types!
Meaning:
The family unit is an intimate domestic grouping fabricated up of people related to one another by bonds of claret, sexual mating or legal ties. It is the smallest and most basic social unit, which is also the most important primary group institute in any society.
It is the simplest and near elementary group constitute in a society. Information technology is a social group consisting of a begetter, female parent and i or more children. Information technology is the most immediate group a child is exposed to. In fact, it is the virtually enduring group, which has tremendous influence on the life of an individual, from birth until decease. It also accounts for the most enduring social relationship plant in society. Family has been defined by different social scientists.
Some of these definitions are given below:
'Family is a group defined by sexual human relationship, sufficiently precise and enduring to provide for the procreation and upbringing of children.'
– Maclver
'The family, almost without question, is the most of import of any groups that human being experience offers … the family … is with u.s.a. always, or more than precisely, we are with it.'
– Robert Bierstedt
'Family is a more or less durable association of husband and wife, with or without child, or of a man or woman lonely, with children.'
– Grand. F. Nimkoff
'Family unit is the biological social unit composed of husband, wife and children.'
– Eliot and Merrill
'Family is a group of persons united by ties of matrimony, blood or adoption constituting a unmarried household interacting and inter-communicating with each other in their respective social roles of hubby and wife, father and mother, son and girl, blood brother and sister, creating a common culture.'
– Burgess and Locke
'Family unit is a group of persons, whose relations to 1 another are based upon consanguinity and who are therefore kin to one another.'
– Kingsley Davis
Characteristics of Family :
one. Family unit is a Universal group. Information technology is found in some form or the other, in all types of societies whether primitive or mod.
2. A family is based on wedlock, which results in a mating relationship between ii adults of opposite sex.
3. Every family unit provides an private with a name, and hence, it is a source of nomenclature.
4. Family is the group through which descent or beginnings tin be traced.
5. Family is the most important group in any individual'south life.
half-dozen. Family is the nearly basic and important group in principal socialization of an individual.
7. A family is by and large limited in size, even large, joint and extended families.
8. The family is the most important group in club; information technology is the nucleus of all institutions, organizations and groups.
nine. Family is based on emotions and sentiments. Mating, procreation, maternal and fraternal devotion, honey and affection are the basis of family ties.
10. The family is a unit of emotional and economical cooperation.
11. Each fellow member of family shares duties and responsibilities.
12. Every family unit is made up of husband and married woman, and/or one or more than children, both natural and adopted.
xiii. Each family is made up of different social roles, like those of husband, married woman, mother, father, children, brothers or sisters.
Functions of Family unit:
Equally a social grouping and every bit an important social establishment, family performs various functions that are as follows:
1. Family is a unit of measurement through which procreation takes place. Marriage sanctions sexual relationships, and it also establishes a family unit, which is further reinforced with the birth of children.
two. The process of reproduction is institutionalized, regulated and controlled in a family. The family unit legitimizes the deed of reproduction.
three. Family helps in propagation of homo species and perpetuation of human race.
4. Family provides an individual with an identity.
5. It is through the family that every family name is carried on from one generation to some other.
half dozen. Family is responsible for the production and upbringing of children.
7. Family unit is an important agent of socialization. The chief socialization of any private takes place within the family. The immediate family members teach all the basic rules and norms of social life to a child.
8. Family is also an of import agent of cultural transmission. Civilization is transmitted from ane generation to another through family. All the aspects of culture are learnt within the family construction.
9. Family is a great source of strength, emotional and psychological, for its members. All the members are aware that they can depend upon their family unit in the times of need.
10. Family provides an individual with a home, and establishes indelible social relationships.
xi. The family is the basis of division of labour, where all members have their duties and obligations towards each other.
12. A family fulfills the economic needs of its members. This function has undergone transformation, with families moving from being production and consumption units in earlier times, to becoming more of consuming units rather than a producing ane. At present-a-days, members of a family no longer produce things themselves; rather, they go out and piece of work for some monetary remuneration or wages.
xiii. Family is traditionally responsible for the education of the children.
14. Family unit as well has a recreational role. Earlier, nearly recreation was family- based. Family gatherings during festivals, functions, family reunions, marriages, brought entire families together. Now-a-days, taking family members out on holidays or for movies, plays, dinners, or parties, etc., perform the same function.
Types or Forms of Family :
We shall look at some of the types of family in this section (Effigy 1).
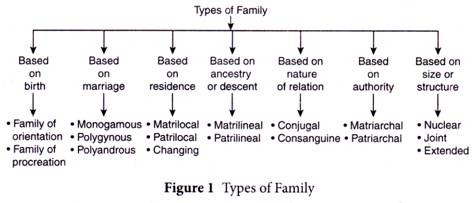
A description of the above classification of types or forms of family is explained here:
1. Based on Birth:
Family of Orientation:
The family in which an individual is born is his family of orientation.
Family of Procreation:
The family unit where an individual sets upwards after his/her marriage is his/her family of procreation.
The family of orientation and procreation may alive together under the same roof, but can still exist distinguished.
2. Based on Marriage:
Monogamous Family:
This family consists of one husband and wife, including children and is based on monogamous marriages.
Polygynous Family:
A family unit consisting of one husband, and more than one wife, and all the children born to all the wives or adopted past each of them. This type of family has its basis in the polygynous course of marriage.
Polyandrous Family unit:
A family made up of 1 married woman and more than i husband, and the children, either born or adopted with each one of them. This family is based on polyandrous wedlock.
3. Based on Residence:
Family of Matrilocal Residence:
When a couple stays in the wife'southward house, the family is known as family of matrilocal residence.
Family of Patrilocal Residence:
When a family unit stays in the house of husband, the family is known every bit family unit of patrilocal residence.
Family of Changing Residence:
When a family stays in the husband's house for some fourth dimension, and moves to wife's house, stays at that place for a period of fourth dimension, and then moves back to husband'due south parents, or starts living in another place, the family is called a family of changing residence.
four. Based on Beginnings or Descent:
Matrilineal Family unit:
When ancestry or descent is traced through the female person line, or through the mother'due south side, the family is called matrilineal family.
Patrilineal Family:
A family in which the authority is carried down the male line, and descent is traced through the male person line or the begetter's side, is called a patrilineal family.
5. Based on Authorization:
Matriarchal Family:
Matriarchal families are generally found in matrilineal societies. In these families, a woman is the head of the family, and authority is vested in her. Succession of belongings is through the female person line, i.e., simply daughters inherit the belongings.
After marriage, the husband resides in the wife'due south house and descent is traced through the mother's side. Here, children are brought up in mother'southward business firm. Thus, in matriarchal societies, the matrilocal system exists. Matriarchal families are found only in matrilineal societies, which are very express in number all over the earth. They are found in parts of Latin America, Ceylon, parts of Africa and India (the Khasis and the Garos).
Patriarchal Family unit:
Patriarchal families are commonly found in all parts of the world, since most societies in the globe are patrilineal societies. In patriarchal families, the caput of the family unit is a male, and say-so is vested in him. Descent and property is passed through the male line and children are brought upwards in begetter's business firm. Such families are patrilocal in nature.
6. Based on the Nature of Relations:
Conjugal Family:
The conjugal family is fabricated up of adults among whom there is a sexual relationship. It refers to a family unit organization of spouses and their dependent children. The emphasis is placed on the marital relationship that exists between spouses. In modern times, the term 'conjugal family' is being used for partners, who have a long- term sexual relationship, but are not actually married.
Consanguine Family unit:
A consanguine family unit is made up of members among whom a blood relation exists, or those who are consanguineal kin, i.e., a family consisting of parent(southward) and children, or siblings (brothers, sisters, or brothers and sisters).
7. Based on state or structure:
Nuclear Family:
A nuclear family is a small group consisting of a husband, a wife and children, natural or adopted. It is more or less an democratic unit that is not nether the command of adults or elders of the family. It consists of two generations only. In all mod societies, nuclear family is the most common type of family. In fact, nuclear family is both the upshot too every bit the cause of the disintegration of articulation family.
Articulation Family:
A joint family consists of three generation, living together under the same roof, sharing the aforementioned kitchen and bag or economic expenses. It is a family unit consisting of three nuclear families living together. According to Iravati Karve, a joint family is 'a group of people, who mostly live under the same roof, who eat food cooked at one hearth, who hold property in common, and who participate in mutual family worship and are related to each other as some detail blazon of kindered.'

In Figure 2, Ego (the shaded figure) is a part of a joint family consisting of four generations—the children, parents, grandparents and nifty-grandparents, all from the fathers side. These types of joint families are also known as patriarchal (father- centred) or patrilineal (lineage traced through the father s or male person side) articulation families.
In such families, only unmarried daughters, or at times widowed daughters are a office of the family. Married daughters no longer belong to the family unit as they become a role of their husbands family unit. However, in the case of matriarchal articulation families (mother-centered) or matrilineal (lineage or descent traced through the mothers side or the female person side), daughters are a office of the articulation family, whereas sons become a part of their wives' families.
Source: https://www.yourarticlelibrary.com/speech/family-meaning-characteristics-function-and-types/34966
0 Response to "Describe the Characteristics of Four Different Family Structures"
Post a Comment